Alcoholism
The Growing Trend of Alcoholism in America
 Americans today are drinking a lot more than they were a few years back. This disturbing trend has potential drastic implications for the future health care costs of the country. A study published in JAMA psychiatry found that the number of binge drinking adults who indulge in alcohol at least once every week might be as high as 30 million. This number exceeds the population of every American state except for California. An identical number of people reported of abusing alcohol or being dependent. Based on the same report, women were shown to have a larger increase in alcoholism.
Americans today are drinking a lot more than they were a few years back. This disturbing trend has potential drastic implications for the future health care costs of the country. A study published in JAMA psychiatry found that the number of binge drinking adults who indulge in alcohol at least once every week might be as high as 30 million. This number exceeds the population of every American state except for California. An identical number of people reported of abusing alcohol or being dependent. Based on the same report, women were shown to have a larger increase in alcoholism.
Clearly, alcohol poses a serious problem in today’s world. This means that public understanding and knowledge of the effects and symptoms of alcoholism is very important in order to decrease the statistics. These numbers show an increase in the fatalities, diseases, and injuries associated with alcoholism in America. The best way to reduce the number of people negatively affected by alcohol abuse is to educate them on the associated dangers. Friends and family of individuals who are alcoholics should realize these effects.
Approximately two-thirds of the population in America drinks alcohol but only ten percent of these drinkers consume half of all the alcohol being taken in the country!
One in every 13 adults in America has an alcoholism problem or abuses alcohol. Additionally, several million more Americans engage in unhealthy alcohol consumption with the potential for developing into alcohol abuse. More than three million teenagers in America from age 14 to 17 have a drinking problem. Youth drinkers who started taking alcohol before age 15 were compared to adults who started drinking at around age 21. The youth were found to be twice as likely to start abusing alcohol and four times more likely to become alcohol dependent. In fact, 62% of underage high schoolers admitted to being drunk at some point while 31% of them admitted to have drank an excess of five drinks over 2 weeks. The number of 17-year-old Americans or younger who were engaged in heavy consumption of alcohol reduced by two-thirds between the years 1985 and 1987. Even though the number continues to decline, underage consumption of alcohol remains to be a problem in America.
In 2009, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention found that almost 51 percent of adults in America were regular current drinkers and they had taken at least 12 drinks within the past year. 13.6 percent of American adults were infrequent current drinkers and they had taken between one and eleven drinks within the past year. The bad news is that more than 7% of the population in America aged 18 years and above has a drinking problem. this approximates to roughly 13.8 million Americans with 8.1 million out of this number being alcoholics. According to these numbers, it is quite evident that alcohol abuse and alcoholism are serious issues affecting millions of people.
The number of people going through treatment for alcohol-related issues such as alcoholism is high, but not as high as that of the people experiencing these issues. For example, in the year 1997, only 3.1 million Americans were this treatment with most of them aged between 26 and 34. Nevertheless, more than 3 million seniors in America are currently struggling with genuine drinking problems if not alcoholism.
Alcohol abuse and alcoholism also appear to affect more men compared to women. In fact, even though 3.9 million women in America are problem drinkers, there are almost 9.8 million men, which is 3 times the number of women, who are alcoholics. Regardless, women should watch their alcohol consumption because they can become more inebriated eve if they take the same amount of alcohol compared to men. Additional research found that women have a higher likelihood of experiencing alcohol-related problems compared to men i.e. depression, unwanted sexual advances, and abusive relationships.
Women in minority groups also have a higher likelihood of experiencing problems caused by alcohol abuse. Some lesbians, for example, will use alcohol to help them cope with the stigma associated with being gay not to mention their internalized homophobia. 25% of women who are dealing with eating disorders are also struggling with alcohol abuse. The highest drinking rates lie among Latina highs school students with 56 percent consuming more than five drinks within a short period. Additionally, 13 percent out of black students within the same age bracket also report heavy consumption of alcohol while 40 percent of Indian adult women in America have become alcohol-dependent.
An estimate of 53 percent of Americans has one close relative who have problems of alcohol dependency. 43 percent of adults in America have seen the problem of alcoholism in their families as something they have experienced with a partner/spouse, or as something they have grown up seeing. It has been currently estimated that 6.6 million children under 18 years of age are living with a parent dealing with alcoholism.
Each year, 79000 deaths in America can be attributed to alcohol problems. This makes alcohol the third primary cause of preventable deaths in the US. Alcohol is closely followed by diet and activity problems and tobacco. The number of alcohol-related deaths might be fewer than the number of deaths caused by cancer or heart disease, but these deaths have a tendency to affect much younger individuals. Alcohol problems also cost money just as much as they cost lives. Alcoholism and alcohol abuse in America resulting in violent crimes, medical care, lost production, motor vehicle accidents, and the need for social programs costs Americans roughly forty-sixty billion every year.
Excessive use of alcohol each year results in the loss of approximately 2.3. million years of potential life averaging a potential production time, loss of 30 years for every fatality caused. In 2005, there were more than 1.6 million cases of hospitalization and more than 4 million visits to the emergency room because of various alcohol problems.
A third of deaths caused by alcohol problems occur in the form of suicides and accidents such as motor vehicle crashes, drowning incidents, and head injuries. Almost 20 percent of victims of suicide in the US are alcoholic while 41 percent of fatal traffic incidents in the country are related to problems with alcohol. Every 48 minutes, there are alcohol-related car accidents occurring in the United States and the result of this is 30 deaths for each day. Out of all the traffic accidents and suicides occurring in the US, half of these result in fatalities while a third of the injuries resulting are alcohol abuse related. The people who are at a higher risk for involvement in alcohol-related crashes include drivers and motorcyclists with prior convictions for DUIs and teen drivers. 10,389 people died in 2009 because of car crashes caused by drivers whose cognition was impaired by alcohol. This number represents approximately one-third of all the traffic-related deaths that occurred in the United States in that year. Every year, motor vehicle crashes in the United States that are alcohol related cost the US more than 51 billion dollars.
What are the Consequences of Alcoholism?
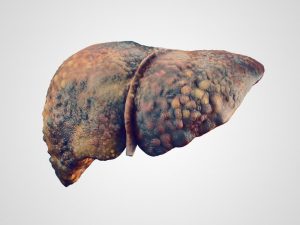 Liver disease is one of the biggest health issues caused by excessive drinking. In the year 2009, the number of deaths caused by alcoholic liver disease came to a whopping 15,183. Excluding accidents and homicides, the number of deaths related to alcohol problems was 24,518.
Liver disease is one of the biggest health issues caused by excessive drinking. In the year 2009, the number of deaths caused by alcoholic liver disease came to a whopping 15,183. Excluding accidents and homicides, the number of deaths related to alcohol problems was 24,518.
Binge drinking is described as a pattern, bringing one’s concentration level of blood alcohol to 0.08 grams or more. National surveys found that approximately 92 percent of adults in America reported of having been involved in binge drinking in the past month. Even though most binge drinkers are not alcohol-dependent, they are highly likely to develop more health problems. The unfortunate thing about this fact is that most of the people who engage in this are especially young and between 18 and 20 years old. Ninety percent of the alcoholic drinks that are taken by teenagers are binge drinks. Excessive underage drinking produces a number of consequences affecting college students all over the US, regardless of whether they choose to drink or not.
Vandalism: 11 percent of college students who drink admitted to having damaged some property while under the influence of alcohol
Unsafe sex: Out of the 18 to 24 year-old 400,000 college students who engage in unprotected sex, a quarter of this number reported of being too intoxicated at the time to remember if they had issued their consent.
Sexual abuse: According to Hingson et al, approximately 97,000 of college students between the age of 18 and 24 are date rape and sexual assault victims as a result of alcohol use
Property Damage: Most colleges in America have moderate to significant problems with property damage caused by alcohol use. These claims are more than 25 percent of college administrators with elevated drinking levels and more than 50 percent of college administrators with reduced drinking levels.
Involvement with Police: 2002 data that was published by Wechsler et al. determined that 5 percent of college students became involved with campus security or police at one point during their time in college because of their alcohol consumption. In the same year, Hingson et al corroborated that 110,000 college students between the ages of 18 to 24 were arrested for violations related to alcohol misuse i.e. public drunkenness or driving under the influence
Injury: Hingson et al reported that in 2009, 599,000 young adults aged between 18-24 years in college were injured unintentionally while under the influence of alcohol.
Suicide Attempts and Health Problems: As 150,000 students deal with health problems caused by alcohol abuse, 1.2 to 1.5 percent claimed to have attempted drug or alcohol-related suicide within the previous year in 1998
Drunk driving: a study published by Hingson et al in 2009 found that 3,360,000 students between the ages of 18 and 24 years drive while under the influence of alcohol
Death: Data published in 2009 stated that 1825 college students between the ages of 18 and 24 years lose their lives because of unintentional injuries that are alcohol-related
Assault: In the year 2009, 696,000 students between the ages of 18 and 24 years were victims of assault with the perpetrators in the said cases being other students who had also been drinking
Alcohol dependence and abuse: Reports conducted by Knight et al in 2002 found that 31 percent of students at the college level were identified as having an alcohol abuse problem while six percent indicated alcohol dependent behavior
Academic Problems: Out of the college students who indulge in alcohol, almost 25 percent reported doing badly on exams and papers, missing class, and falling behind in the year 2002. As a result, these students received low grades
The above-mentioned consequences of alcohol abuse show that there is a significant correlation between alcohol use and crime. Approximately three million crimes of a violent nature happen every year in the US, Out of this number, thirty-five percent involve offenders who were drinking during the time of the crime. Two-thirds of victims of partner or domestic violence reported of alcohol having been involved. In cases like these, three out of four incidents of spousal violence included an offender who was inebriated or drunk at the time. According to the Federal Bureau of Investigation’s National Incident-based Reporting System, seven out of ten violent alcohol-related incidents that occurred in 1995 usually happened within a residence and frequently at 11 p.m.
Health Problems
 There are different health problems that are related to alcoholism and alcohol-abuse, but they are of the uttermost concern due to their severity. A Harvard Medical School Study demonstrated a connection between breast cancer and moderate drinking in 100,000 women or more. Additionally, 9.6 percent of adults in America living with mental disorders are alcohol-dependent. Excessive drinking can deplete one’s brain cells over time, diminish energy levels, and disrupt the sleep cycle. It also causes the brain to block its ability to create and learn new memories. An alcohol user engaging in binge drinking can destroy his/her brain’s capacity to retain new verbal information. This is because binge drinking has adverse effects on verbal declarative memory.
There are different health problems that are related to alcoholism and alcohol-abuse, but they are of the uttermost concern due to their severity. A Harvard Medical School Study demonstrated a connection between breast cancer and moderate drinking in 100,000 women or more. Additionally, 9.6 percent of adults in America living with mental disorders are alcohol-dependent. Excessive drinking can deplete one’s brain cells over time, diminish energy levels, and disrupt the sleep cycle. It also causes the brain to block its ability to create and learn new memories. An alcohol user engaging in binge drinking can destroy his/her brain’s capacity to retain new verbal information. This is because binge drinking has adverse effects on verbal declarative memory.
The misuse of alcohol can cause death from multiple ailments resulting from it such as type II diabetes, pancreatitis, some types of cancer, infections, injuries, liver cirrhosis, stroke, cardiovascular diseases, hypertension, and fetal alcohol spectrum disorders.
If alcoholism continues to grow as a trend within the next four years, there is a risk of the number of deaths in America reaching well over 100,000.
Who Do We Determine to Be an Alcoholic?
For one to be diagnosed as an alcohol abuser, he or she must have shown at least one of the below characteristics.
- Frequent alcohol use which results in a failure to accomplish primary role obligations at home, school, or work. This could manifest as the neglect of one’s household or children, school expulsions or suspensions, absences related to alcohol, poor work performance, or repeated absences
- Frequent use of alcohol in physically hazardous situations such as operating machinery or driving an automobile when one’s cognitive abilities are impaired by alcohol
- Frequent occurrence of legal problems that are alcohol-related such as arrests for disorderly conduct while under the influence of alcohol
- Persistent alcohol use despite experiencing recurrent or continued interpersonal or social problems worsened or caused by the effects of alcohol i.e. arguments with one’s significant other or spouse regarding their consequences of intoxication.
For an individual to be diagnosed as alcohol-dependent, he or she must have at least 3 out of the below seven symptoms.
- A need for considerably increased alcohol amounts in order to achieve the desired effect or intoxication or a distinctly diminished effect associated with the continuous use of the same alcohol amount
- The distinguishing alcohol withdrawal syndrome or drinking to avoid or relieve withdrawal symptoms if not using a substance that is closely related
- Drinking larger amounts of alcohol or drinking over a longer period than is intended
- The perpetual desire or unsuccessful efforts to control or cut down one’s drinking habits
- Giving up or reducing of important recreational, occupational, or social activities because of drinking
- Spending a lot of time engaging in activities necessary to recover, use, or obtain the effects of drinking
- Continued drinking regardless of knowing that one has a recurrent or persistent psychological or physical problem likely to be aggravated or caused by drinking.
If an individual meets any of the criteria for alcohol dependence or abuse, he or she would be characterized as an alcoholic
What Could Be Driving This Increase In Alcoholism?
The increase in alcoholism in the United States could be caused by despair and stress thus resulting to alcohol use as a means of coping with it all. As mentioned above, the increased occurrence of alcohol use in disorder has been found to be much greater among minority groups than white people. This is a possible reflection of the widening social inequalities following the recession in 2008. It has been said that middle-aged whites in America without college degrees were currently facing ‘deaths of despair’. This includes alcohol-related liver disease, alcohol/drug overdoses, and suicide. The distress caused by rapid technological change and globalization may have been responsible for this deadly outcome. Currently, middle-aged whites are more likely to report problems with mental health and pain compared to their predecessors. They are also experiencing alcoholism symptoms at a younger age.
People who take alcoholic drinks excessively frequently abuse prescription sedatives on the side. Alcohol has been known to heighten the sedative effects brought about by muscle relaxants, sleep medications, antidepressants, anti psychotics, and anti-anxiety drugs like Xanax. These combinations are quite deadly. Xanax and alcohol with both depress the central nervous system thus reducing one’s breathing rate and heart rate not to mention their effects might be interdependent. This means the combined effects of both drugs can exceed the sum of their singular effects.
Treatment
 Alcoholism in America poses a great threat to various aspects of people’s lives and as such it must not be disregarded. Quitting alcohol use is usually difficult and addiction professionals are better equipped to help.
Alcoholism in America poses a great threat to various aspects of people’s lives and as such it must not be disregarded. Quitting alcohol use is usually difficult and addiction professionals are better equipped to help.
Patients of alcoholic abuse and dependency can detox at rehabilitation facilities with 24-hour supervision by a medical team. After admission into rehabilitation, certified physicians will assess patients first in order to examine all the relevant symptoms and offer the right treatment plan depending on the patient’s requirements. Usually, when alcoholics try to detox at home by quitting cold turkey it can fail. This is because the withdrawal symptoms can become too much to bear and he or she goes back to using alcohol or drugs to ease the pain. Trying to detox on your own is also risky.
Following long-term alcohol abuse, withdrawal can cause delirium tremens and seizures and without proper medical care, the patient could become delirious within 72 hours of stopping.
In order to overcome alcoholism, there has to be a comprehensive approach that includes:
- Abstaining from using any substances
- Therapies to address any conditions occurring at the same time
- Development of healthy coping skills
An abstinence-based treatment approach is more beneficial because complete recovery of the individual depends on true sobriety. It will not only address the substance use but also the patient’s whole self. Recovery from alcohol dependency or abuse involves much more than the detoxification aspect. Patients will require plenty of professional support that they will not be able to get at home.
Most addiction professionals consider addiction to be a bio-psycho-social-spiritual disorder in which treatment of all the four aspects is necessary. In order to heal alcoholism in America, there needs to be healing of the spirit, mind, and body. Treating all aspect of this disease can help to prevent ‘death of despair’ and the rehabilitation process can be a trans-formative experience for long-term recovery.
Unfortunately, Americans view excess drinking as more of a character flaw and not a medical problem thus only a fifth of people having reported alcohol dependency or abuse have undergone treatment. There is still some stigma associated with alcoholism and people are still hesitant to talk to their doctor about it.
